The biosynthesis, the way plants make substances themselves, is rather complex. The way in which certain cells in plants (see January 25 post) produce essential oil too. To be able to follow this story some knowledge of chemistry and biochemistry is required.
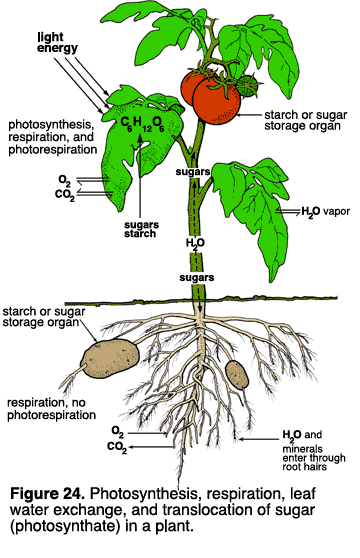
A plant is using photosynthesis to make glucose. Plants use glucose for combustion or stored as starch. Photosynthesis takes place in the chloroplasts.
The combustion of glucose (glycolysis), which runs a number of steps, gives energy and releases water and carbon dioxide.
These reactions take place largely in the mitochondria. In these reactions, two substances are formed that are important for the formation of terpenes.
Terpenes are the main constituents of the essential oil.
Terpenes are the main constituents of the essential oil.

These two substances are glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate and pyruvate. Through several steps and by specific enzymes is ultimately formed IPP and DMAPP. The following step is the formation of GPP, geranyl diphosphate. See below:
IPP stands for isopentenyl pyrophosphate and DMAPP for dimethylallyl pyrophosphate. There are two places where the formation of IPP and DMAPP reactions take place. Schedule A: in the cytosol (cytoplasm) and Schedule B: in a plastid.
IPP and DMAPP (isoprenes) are the building blocks for the formation of numerous terpenes.
All terpenes are derived from the condensation of 5 - carbon unit isopentenyl diphosphate (IPP) and its isomer dimethylallyl diphosphate (DMAPP). Depending on the number of isoprene units that are tied together terpenes are classified on the number of C atoms: hemiterpenen (C5), monoterpenes (C10), sesqui-(C15), di-(C20), Sester-, tri-, and tetra-terpenes (C25, C30, C40, respectively).
The above diagram shows how the terpenes from IPP and DMAPP are formed. This is basically how the biosynthesis of terpenes proceeds. (click the left mouse button on the picture or diagram to enlarge)
There are also many species-specific biosyntheses such as in caraway seed. From geranyl diphosphate to the enzyme limoneensynthase limonene (a monoterpene) is formed. Through two other enzymes limonene may again be converted into carvone. This brief story I could write after reading articles about it on the internet.
Articles published on: http://www.plantphysiol.org/cgi/content/full/135/4/1893#top#top
and the many charts on this subject available on the internet
Among others, this thesis research on lavender:
Monoterpene production and regulation in Lavenders (Lavandula angustifolia and Lavandula x intermedia) by Astrid Boeckelmann; downloadable via: https://circle.ubc.ca/bitstream/handle/2429/2804/ubc_2008_fall_boeckelmann_astrid.pdf?sequence=1
Articles published on: http://www.plantphysiol.org/cgi/content/full/135/4/1893#top#top
and the many charts on this subject available on the internet
Among others, this thesis research on lavender:
Monoterpene production and regulation in Lavenders (Lavandula angustifolia and Lavandula x intermedia) by Astrid Boeckelmann; downloadable via: https://circle.ubc.ca/bitstream/handle/2429/2804/ubc_2008_fall_boeckelmann_astrid.pdf?sequence=1








True terpenes the scent of most plants is because of a blend of terpenes. In nature, these terpenes shield the plants from creature brushing or irresistible germs. True terpenes
ReplyDelete